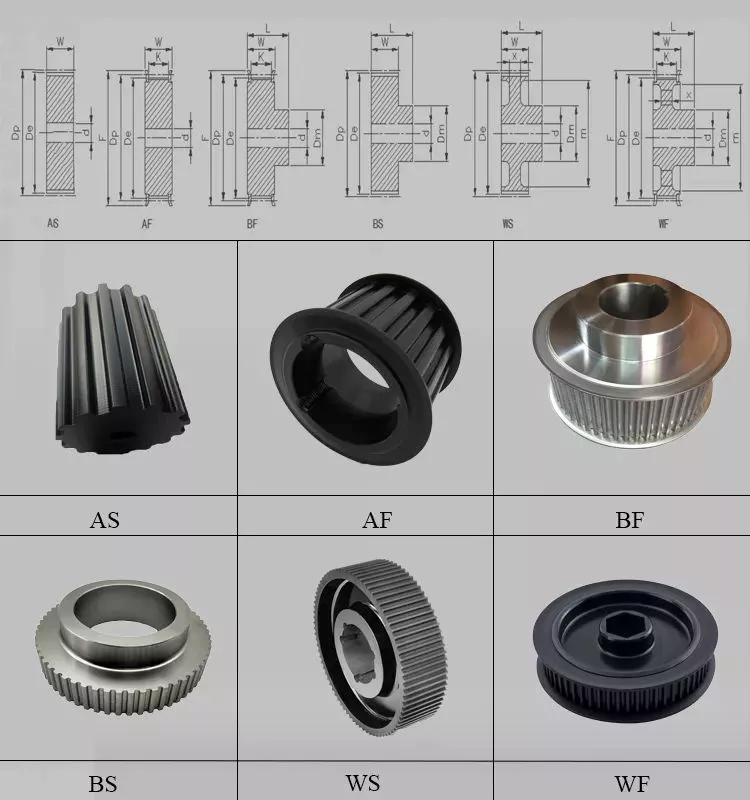
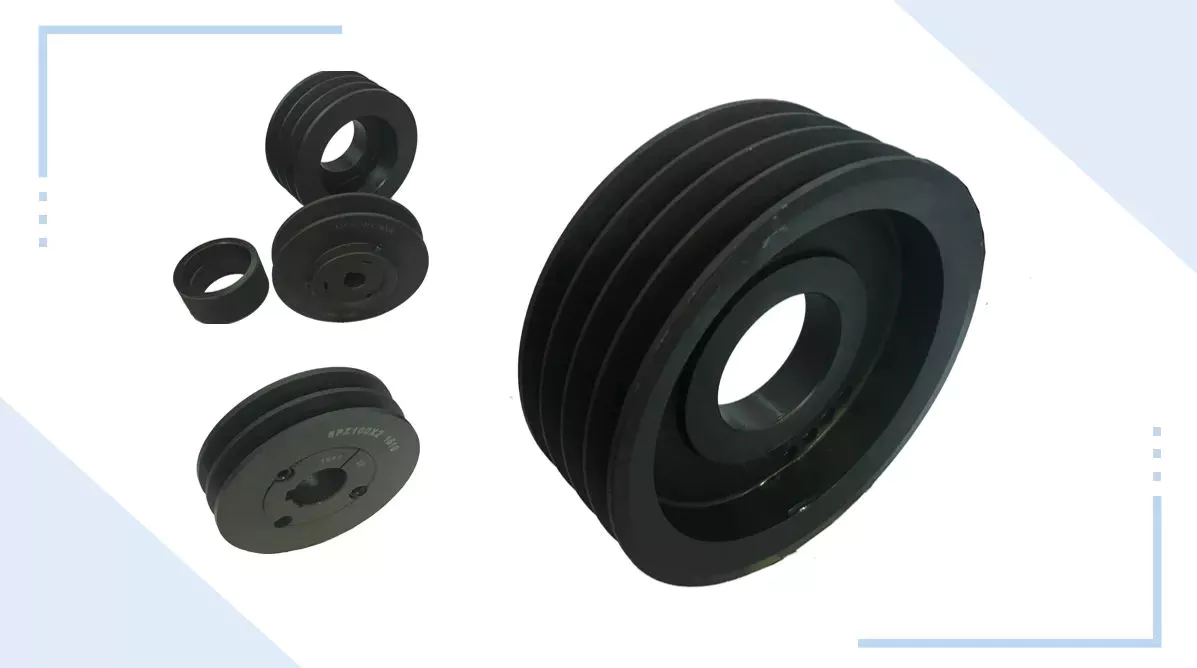
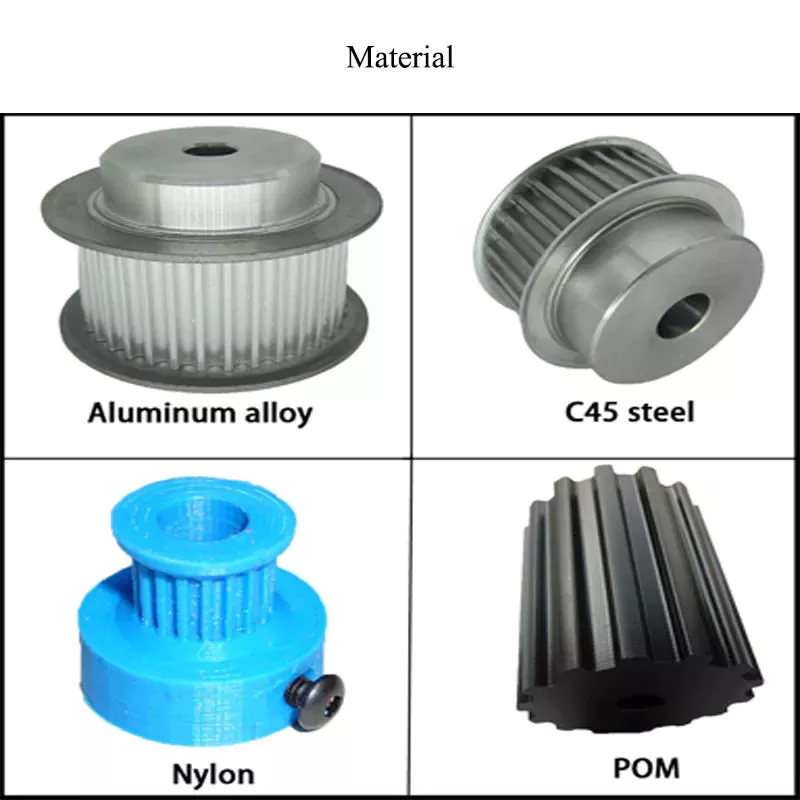
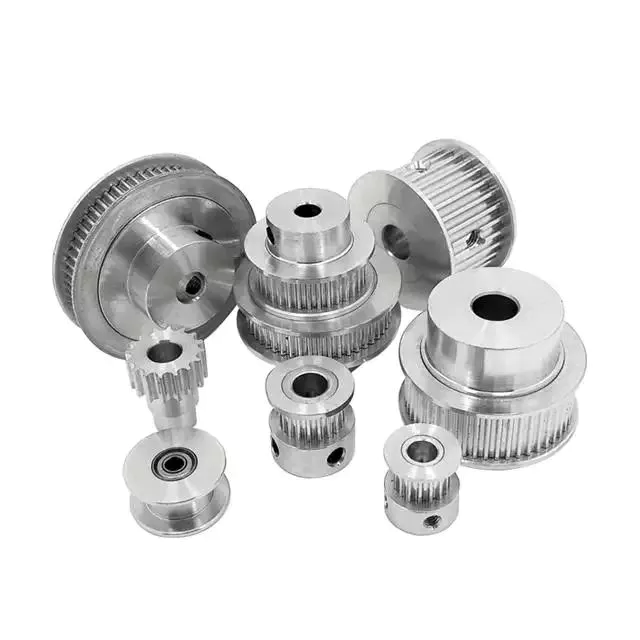
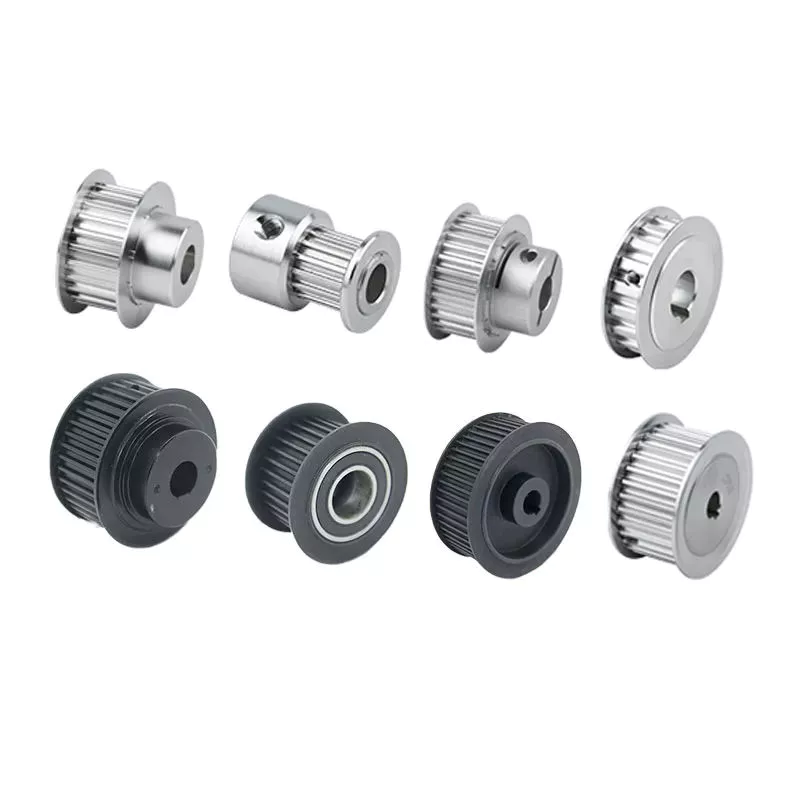
Product Description
V Belt Pulley with ISO9001 (SPA, SPB, SPC, SPZ)
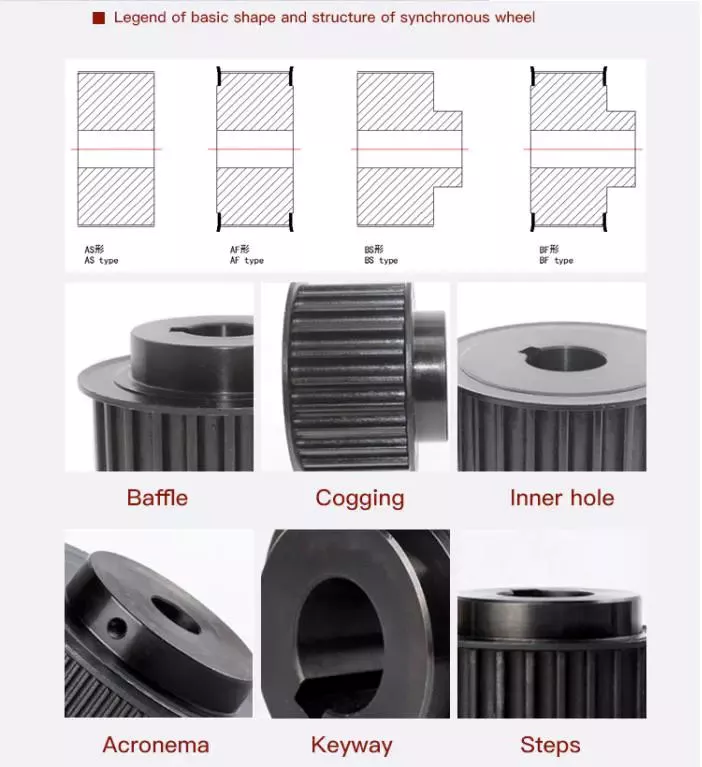
1. V-Pulley
Taper Bore
SPZ SPA CHINAMFG SPC
2. V-Pulley
Stock Bore
SPZ SPA CHINAMFG SPC
3. V-Pulley
Adjustable Speed
TB-1 TB-2 SB-1 SB-2
4. V-Pulley
Multi-Wedged
J L M
| 50 – 1 x SPZ – 1008 rü 15 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 56 – 1 x SPZ – 1008 rü 15 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 60 – 1 x SPZ – 1008 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 63 – 1 x SPZ – 1108 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 67 – 1 x SPZ – 1108 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 71 – 1 x SPZ – 1108 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 75 – 1 x SPZ – 1108 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 80 – 1 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 85 – 1 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 90 – 1 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 95 – 1 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 100 – 1 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 106 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 112 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 118 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 125 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 132 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 140 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 150 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 160 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 170 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 180 – 1 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 190 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 200 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 224 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 250 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 280 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 315 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 355 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 400 – 1 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 500 – 1 x SPZ – 2517 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 50 – 2 x SPZ – 1008 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 56 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 60 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 63 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 67 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 71 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 75 – 2 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 80 – 2 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 85 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 90 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 95 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 100 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 106 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 112 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 118 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 125 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 132 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 140 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 150 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 160 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 170 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 180 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 190 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 200 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 224 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 250 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 280 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 315 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 355 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 400 – 2 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 450 – 2 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 500 – 2 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 63 – 3 x SPZ – 1108 rü 17 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 67 – 3 x SPZ – 1108 rü 17 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 71 – 3 x SPZ – 1108 rü 17 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 75 – 3 x SPZ – 1210 rü 14 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 80 – 3 x SPZ – 1210 rü 14 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 85 – 3 x SPZ – 1610 rü 14 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 90 – 3 x SPZ – 1610 rü 14 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 95 – 3 x SPZ – 1610 rü 14 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 100 – 3 x SPZ – 1610 rü 14 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 106 – 3 x SPZ – 1610 rü 14 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 112 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 118 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 125 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 132 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 140 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 150 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 160 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 170 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 180 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 190 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 200 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 224 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 250 – 3 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 280 – 3 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 315 – 3 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 355 – 3 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 400 – 3 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 450 – 3 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 500 – 3 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 630 – 3 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 63 – 4 x SPZ – 1108 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 67 – 4 x SPZ – 1108 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 71 – 4 x SPZ – 1108 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 75 – 4 x SPZ – 1210 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 80 – 4 x SPZ – 1210 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 85 – 4 x SPZ – 1610 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 90 – 4 x SPZ – 1610 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 95 – 4 x SPZ – 1610 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 100 – 4 x SPZ – 2012 rü 20 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 106 – 4 x SPZ – 2012 rü 20 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 112 – 4 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 118 – 4 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 125 – 4 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 132 – 4 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 140 – 4 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 150 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 160 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 170 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 180 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 190 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 200 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 224 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 250 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 280 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 315 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 355 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 400 – 4 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 450 – 4 x SPZ – 3571 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 500 – 4 x SPZ – 3571 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 630 – 4 x SPZ – 3030 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 800 – 4 x SPZ – 3030 e.b. | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 85 – 5 x SPZ – 1610 rü 38 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 90 – 5 x SPZ – 1610 rü 38 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 95 – 5 x SPZ – 1610 rü 38 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 100 – 5 x SPZ – 2012 rü 32 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 106 – 5 x SPZ – 2012 rü 32 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 112 – 5 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 118 – 5 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 125 – 5 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 132 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 140 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 150 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 160 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 180 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 200 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 224 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 250 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 280 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 315 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 355 – 5 x SPZ – 2517 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 400 – 5 x SPZ – 3571 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 450 – 5 x SPZ – 3571 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 500 – 5 x SPZ – 3030 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 630 – 5 x SPZ – 3030 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 100 – 6 x SPZ – 2012 rü 44 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 106 – 6 x SPZ – 2012 rü 44 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 112 – 6 x SPZ – 2012 rü 44 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 118 – 6 x SPZ – 2517 rü 31 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
Choose GOODLUCK(TAI)
1. Our company boasts a combination of research and development, production and sales with highly professional capabilities.
2. Our company produces the pulley with the following: Drive can mitigate impact load; Transmission smooth operation, low noise, low vibration; Transmission of simple structure, easy to adjust; Drive for the manufacture and installation precision of pulley, unlike meshing transmission strictly; It has the function of overload protection; Transmission center distance of 2 axis adjusting range is larger.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | ISO |
|---|---|
| Pulley Sizes: | All |
| Manufacturing Process: | Casting |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How does the diameter of a pulley affect its mechanical advantage?
The diameter of a pulley plays a significant role in determining its mechanical advantage. Mechanical advantage refers to the ratio of the output force or load to the input force or effort applied to the pulley system. Here’s how the diameter of a pulley affects its mechanical advantage:
1. Larger Diameter: When the diameter of a pulley increases, the mechanical advantage also increases. A larger diameter means that the circumference of the pulley is greater, allowing a longer length of rope or belt to be wrapped around it. As a result, a larger pulley requires less effort force to lift a given load. This is because the load is distributed over a greater length of rope or belt, reducing the force required to overcome the load.
2. Smaller Diameter: Conversely, when the diameter of a pulley decreases, the mechanical advantage decreases. A smaller diameter means that the circumference of the pulley is reduced, resulting in a shorter length of rope or belt wrapped around it. As a result, a smaller pulley requires more effort force to lift a given load. This is because the load is concentrated over a shorter length of rope or belt, requiring a greater force to overcome the load.
It’s important to note that while a larger diameter pulley offers a greater mechanical advantage in terms of reducing the effort force required, it also results in a slower speed of the load being lifted. This is because the longer length of rope or belt requires more input distance to achieve a given output distance. On the other hand, a smaller diameter pulley offers a lower mechanical advantage but allows for a faster speed of the load being lifted.
The mechanical advantage of a pulley system can be calculated using the formula:
Mechanical Advantage = Load / Effort
Where “Load” refers to the weight or force being lifted and “Effort” refers to the force applied to the pulley system. By adjusting the diameter of the pulley, the mechanical advantage can be optimized to suit the specific requirements of the application, balancing the effort force and speed of the load being lifted.
What is the role of pulleys in the mining and construction industries?
Pulleys play a vital role in the mining and construction industries, where they are utilized in various applications to facilitate heavy-duty operations, enhance safety, and improve efficiency. Here’s an overview of the role of pulleys in these industries:
1. Conveyor Systems:
In mining and construction, conveyor systems are extensively used to transport bulk materials, such as ores, rocks, gravel, and construction aggregates. Pulleys are integral components of conveyor systems, guiding and supporting the conveyor belts or chains. They help in maintaining tension, reducing friction, and ensuring smooth movement of materials over long distances. The pulleys used in these systems are designed to withstand high loads and harsh environmental conditions.
2. Hoisting and Lifting Equipment:
Pulleys are crucial in hoisting and lifting equipment used in mining and construction activities. Cranes, winches, and lifting systems often incorporate pulley arrangements to provide mechanical advantage and control the movement of heavy loads. The pulleys, along with ropes, cables, or chains, allow for safe and efficient lifting, lowering, and positioning of equipment, materials, and structures at construction sites or in mining operations.
3. Wire Rope Systems:
In mining and construction, wire ropes are extensively used for various applications, including hauling, towing, and lifting heavy loads. Pulleys, known as sheaves, are employed in wire rope systems to guide and redirect the wire ropes. The sheaves help in maintaining proper alignment, reducing wear, and ensuring efficient power transmission. They are commonly used in applications such as cranes, elevators, and wire rope hoists.
4. Crushing and Screening Equipment:
In the mining and construction industries, pulleys are used in crushing and screening equipment. For example, in crushers, pulleys are utilized to drive the rotating motion of the crusher’s jaws or cones, enabling the crushing of large rocks or ores into smaller sizes. Pulleys also play a role in vibrating screens, helping to generate the necessary vibrations that separate and classify materials based on size.
5. Earthmoving and Excavation Equipment:
Pulleys are incorporated into earthmoving and excavation equipment in mining and construction applications. For instance, in excavators or dragline machines, pulleys are used in the cable systems that control the movement of the bucket or shovel. The pulleys help in extending or retracting the cables, allowing for efficient excavation, loading, and material handling.
6. Tensioning and Alignment:
In mining and construction operations, pulleys are utilized for tensioning and alignment purposes. Tensioning pulleys ensure proper tensioning of belts, ropes, or cables, optimizing power transmission and preventing slippage. Alignment pulleys are employed to maintain the correct alignment of belts or chains, reducing wear, minimizing vibrations, and extending the lifespan of the components.
In summary, pulleys play a critical role in the mining and construction industries, contributing to material handling, lifting and hoisting operations, wire rope systems, crushing and screening equipment, earthmoving and excavation machinery, and tensioning and alignment applications. Their use enhances safety, improves efficiency, and enables the execution of heavy-duty tasks in these demanding industries.

What materials are typically used to manufacture pulleys?
Pulleys are manufactured using a variety of materials, depending on the specific application and requirements. Here are some of the materials that are typically used to manufacture pulleys:
1. Metal Alloys: Metal alloys such as steel and cast iron are commonly used to manufacture pulleys. Steel pulleys offer excellent strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Cast iron pulleys are known for their high strength and resistance to impact and shock loads. Metal alloys are preferred in heavy-duty applications where strength and durability are critical.
2. Aluminum: Aluminum is widely used in pulley manufacturing due to its lightweight nature and corrosion resistance. Aluminum pulleys are commonly used in applications that require reduced weight, such as automotive engines, aircraft components, and light-duty machinery. They offer good strength-to-weight ratio and are suitable for applications where weight reduction is a priority.
3. Plastic: Various types of plastics, including nylon, polyurethane, and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), are used to manufacture pulleys. Plastic pulleys are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and offer good resistance to wear and abrasion. They are commonly used in applications where noise reduction, chemical resistance, or non-conductive properties are required. Plastic pulleys are frequently used in conveyor systems, packaging machinery, and small-scale equipment.
4. Composite Materials: Composite materials, such as fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) and carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP), are utilized in the manufacturing of pulleys. These materials offer high strength-to-weight ratios, excellent resistance to corrosion, and good fatigue resistance. Composite pulleys are commonly used in industries such as aerospace, marine, and sports equipment, where lightweight components with exceptional strength are required.
5. Ceramics: In certain specialized applications, pulleys made of ceramics like aluminum oxide (alumina) or silicon nitride are used. Ceramic pulleys offer exceptional hardness, high temperature resistance, and excellent wear resistance. They are primarily used in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, where extreme precision, chemical resistance, and resistance to high temperatures are crucial.
It’s important to note that the choice of material for pulley manufacturing depends on factors such as load capacity, operating conditions, environmental factors, and cost considerations. Manufacturers select materials that provide the necessary properties to meet the specific requirements of the application while considering factors such as strength, durability, weight, and cost.


editor by CX
2024-05-16








