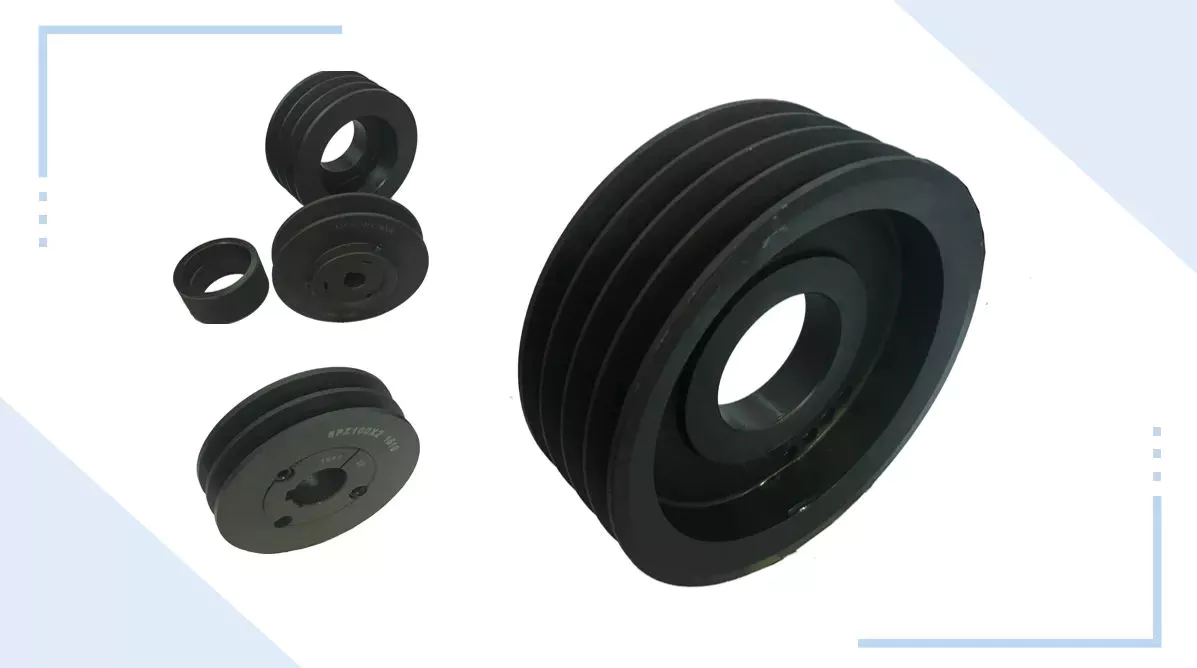
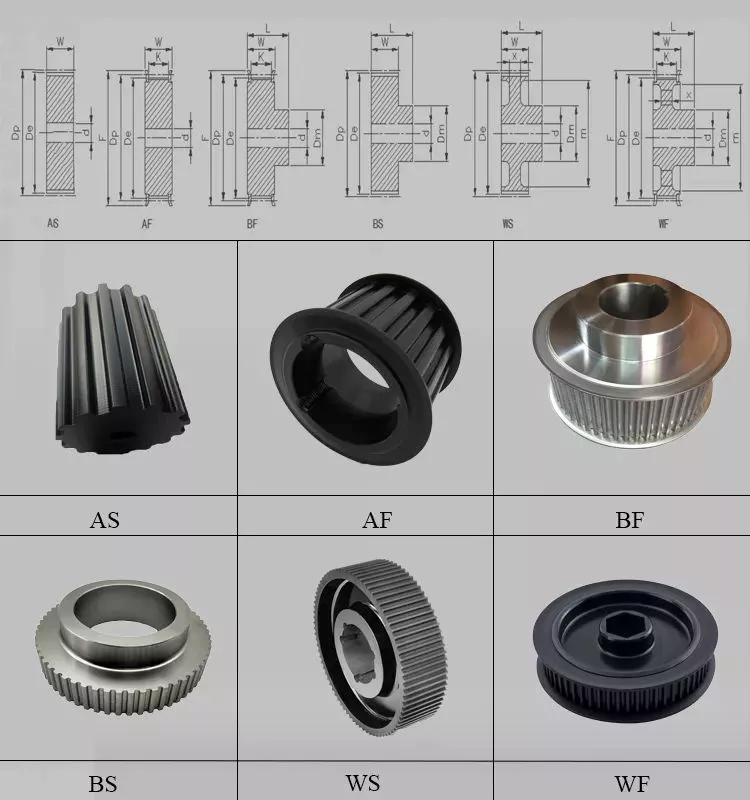
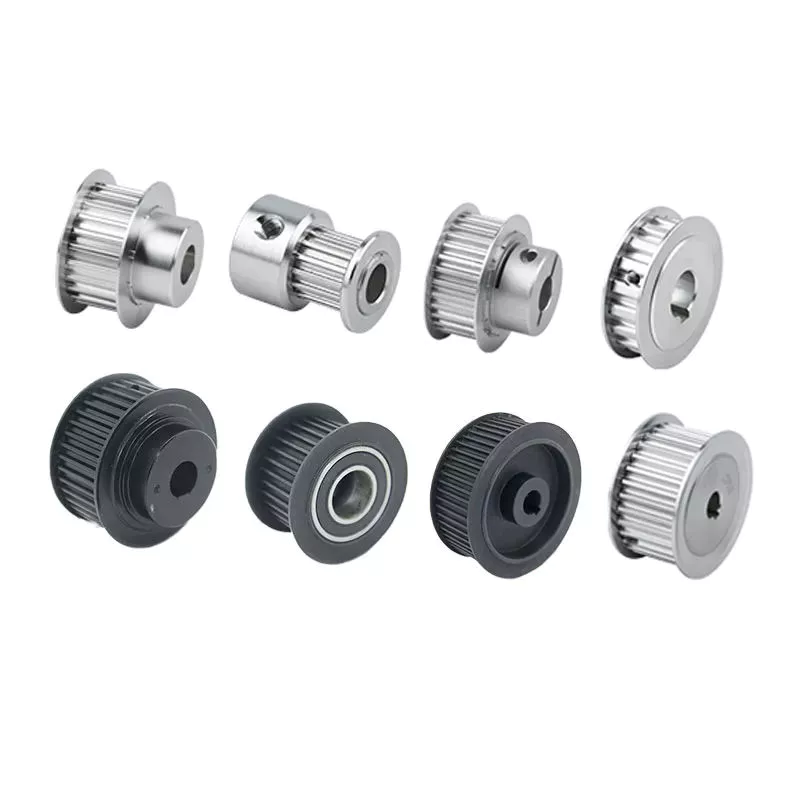
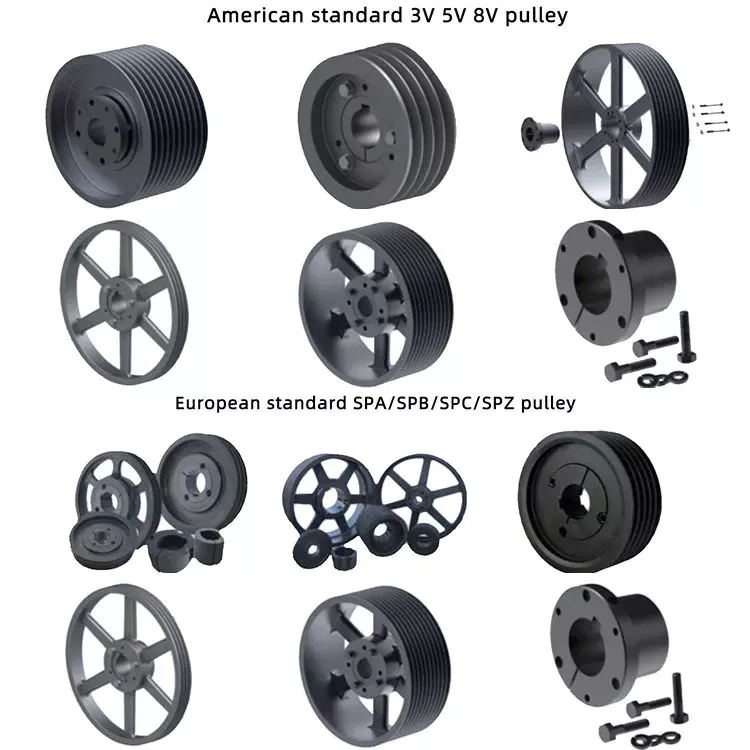
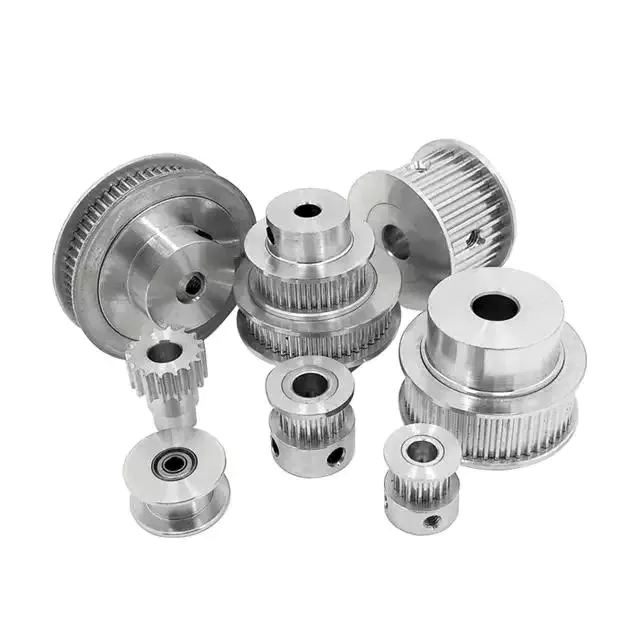
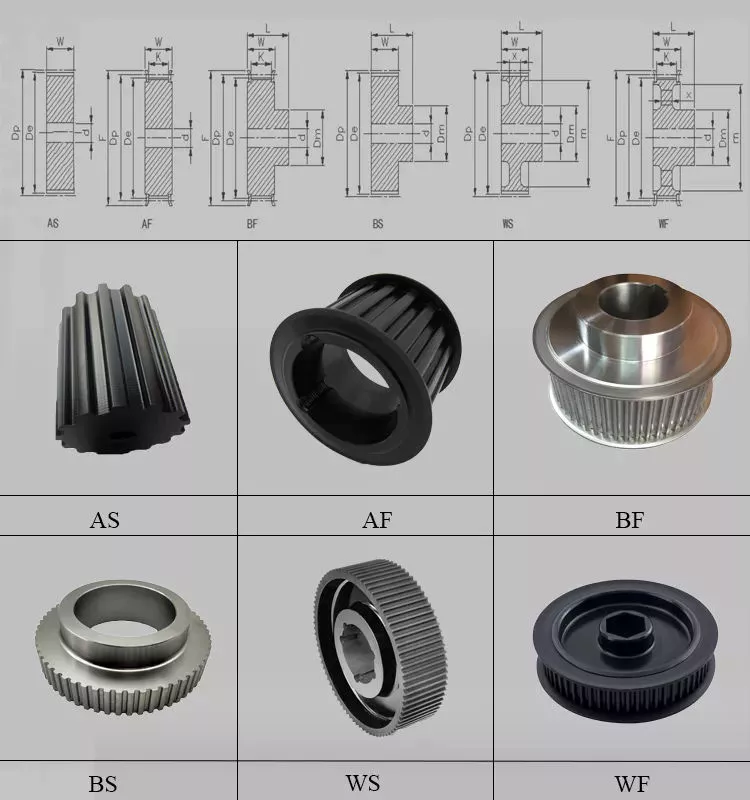
Product Description
Conveyor Pulley is manufactured as per customer requirement,with main design under national standard,quality inspection focusing on shaft core,welded joint,rubber material and hardness,dynamic balance and so on for longer product life time.
| Drive/Head Pulley – A conveyor pulley used for the purpose of driving a conveyor belt. Typically mounted in external bearings and driven by an external drive source. |
| Return/Tail Pulley – A conveyor pulley used for the purpose of redirecting a conveyor belt back to the drive pulley. Tail pulleys can utilize internal bearings or can be mounted in external bearings and are typically located at the end of the conveyor bed. Tail pulleys commonly serve the purpose of a Take-Up pulley on conveyors of shorter lengths. |
| Snub Pulley – A conveyor pulley used to increase belt wrap around a drive pulley, typically for the purpose of improving traction. |
| Take-Up Pulley – A conveyor pulley used to remove slack and provide tension to a conveyor belt. Take-Up pulleys are more common to conveyors of longer lengths. |
| Bend Pulley – A conveyor pulley used to redirect the belt and provide belt tension where bends occur in the conveyor system. |
The specification of pulley:
Drive Drum: is the main component of power transmission. The drum can be divided into single drum (the angle of the belt to the drum is 210 ° ~ 230 °) , Double Drum (the angle of the belt to the drum is up to 350 °) and
multi-drum (used for high power) .
Bend Drum: is used for changing the running direction of the conveyor belt or increasing the surrounding angle of the conveyor belt on the driving roller, and the roller adopts a smooth rubber surface . The drum shaft shall be forgings and shall be nondestructive tested and the inspection report shall be provided.
The Various Surface of Pulley:
Conveyor pulley lagging is essential to improve conveyor belt performance, the combination of our pulley lagging can reduces belt slippage, improve tracking and extends life of belt, bearing & other components.
| PLAIN LAGGING:This style of finish is suitable for any pulley in the conveyor system where watershed is not necessary. It provides additional protection against belt wear, therefore, increasing the life of the pulley. |
| DIAMOND GROOVE LAGGING:This is the standard pattern on all Specdrum lagged conveyor pulleys. It is primarily used for reversing conveyor drive pulleys. It is also often used to allow bi-directional pulley rotation, and the pattern allows water to be dispersed away from the belt. |
| HERRINGBONE LAGGING:The herringbone pattern’s grooves are in the direction of rotation, and offers superior tractive properties. Each groove allows water and other liquids to escape between the face of the drum pulley and the belt. Herringbone grooved pulleys are directional and should be applied to the conveyor in a manner in which the grooves point toward the direction of the belt travel. |
| CHEVRON LAGGING:Some customers specify that the points of the groove should meet – as done in Chevron styled lagging. As before with the herringbone style, this would be used on drive drum pulleys and should be fitted in the correct manner, so as to allow proper use of the pattern and water dispersion also. |
| CERAMIC LAGGING:The Ceramic tiles are moulded into the lagging which is then cold bonded to the drum pulley. This style of finish allows excellent traction and reduces slippage, meaning that the belt tension is lower and, therefore as a result, increases the life of the pulley. |
| WELD-ON STRIP LAGGING: Weld-On Strip Lagging can be applied to bi-directional pulleys, and also has a finish to allow the easy dispersion of water or any fluids between the drum pulley and the belt. |
The Components of Pulley:
| 1. Drum or Shell:The drum is the portion of the pulley in direct contact with the belt. The shell is fabricated from either a rolled sheet of steel or from hollow steel tubing. |
| 2.Diaphragm Plates: The diaphragm or end plates of a pulley are circular discs which are fabricated from thick steel plate and which are welded into the shell at each end, to strengthen the drum.The end plates are bored in their centre to accommodate the pulley Shaft and the hubs for the pulley locking elements. |
| 3.Shaft :The shaft is designed to accommodate all the applied forces from the belt and / or the drive unit, with minimum deflection. The shaft is located and locked to the hubs of the end discs by means of a locking elements. The shaft and hence pulley shafts are often stepped. |
| 4.Locking Elements:These are high-precision manufactured items which are fitted over the shaft and into the pulley hubs. The locking elements attach the pulley firmly to the shaft via the end plates. |
| 5.Hubs:The hubs are fabricated and machined housings which are welded into the end plates. |
| 6.Lagging: It is sometimes necessary or desirable to improve the friction between the conveyor belt and the pulley in order to improve the torque that can be transmitted through a drive pulley. Improved traction over a pulley also assists with the training of the belt. In such cases pulley drum surfaces are `lagged` or covered in a rubberized material. |
| 7.Bearing: Bearings used for conveyor pulleys are generally spherical roller bearings, chosen for their radial and axial load supporting characteristics. The bearings are self-aligning relative to their raceways, which means that the bearings can be ‘misaligned’ relative to the shaft and plummer blocks, to a certain degree. In practical terms this implies that the bending of the shaft under loaded conditions as well as minor misalignment of the pulley support structure, can be accommodated by the bearing. |
The Production Process of Pulley:
Our Products:
| 1.Different types of Laggings can meet all kinds of complex engineering requirements. |
| 2.Advanced welding technology ensures the connection strength between Shell and End-Disk. |
| 3.High-strength Locking Elements can satisfy torque and bending requirements. |
| 4.T-shape End-Discs provide highest performance and reliability. |
| 5.The standardized Bearing Assembly makes it more convenient for the end user to replace it. |
| 6.Excellent raw material and advanced processing technology enable the shaft can withstand enough torque. |
| 7.Low maintenance for continued operation and low total cost of ownership. |
| 8.Scientific design process incorporating Finite Element Analysis. |
Our Workshop:
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Surface Treatment: | Baking Paint |
| Motor Type: | Frequency Control Motor |
| Samples: |
US$ 40/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample Free sample
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do pulleys contribute to the operation of conveyor systems?
Pulleys play a critical role in the operation of conveyor systems by facilitating the movement of materials or products along the conveyor belt. Here’s how pulleys contribute to the functioning of conveyor systems:
1. Power Transmission: Conveyor systems typically utilize a motorized pulley, also known as a drive pulley or head pulley, which is connected to an electric motor. The motor rotates the drive pulley, which in turn moves the conveyor belt. The rotational power from the motor is transmitted to the belt through the drive pulley, enabling the continuous movement of the belt and the materials being conveyed.
2. Belt Tension and Tracking: Pulleys are used to maintain proper tension in the conveyor belt. Tension pulleys, also called idler pulleys, are strategically placed along the conveyor system to apply tension to the belt. These pulleys help to keep the belt taut and prevent slippage or sagging. Additionally, tracking pulleys are used to align the conveyor belt, ensuring it stays centered and runs smoothly along the intended path.
3. Load Support: Pulleys provide support for the conveyor belt and the load it carries. The belt wraps around the pulleys, and the load is distributed over the surface of the belt. Pulleys with larger diameters are often used at points where heavy loads are encountered to help distribute the load more effectively and prevent belt deformation or damage.
4. Directional Changes: Conveyor systems may require changes in direction to accommodate the layout or specific processing needs. Pulleys known as bend pulleys or snub pulleys are used to redirect the belt and change its course. These pulleys are designed to guide the belt smoothly around bends or corners without causing excessive stress or strain on the belt.
5. Speed Control: Pulleys can be utilized for speed control in conveyor systems. By using pulleys of different sizes or by employing variable speed drives, the rotational speed of the drive pulley can be adjusted, affecting the speed at which the conveyor belt moves. This allows for flexibility in the conveyance process, accommodating different material flow rates or specific operational requirements.
6. System Support and Stability: Pulleys, along with their associated support structures, provide stability to the conveyor system. They help to maintain the alignment and tension of the belt, preventing misalignment, vibrations, and excessive belt movement. Properly designed and maintained pulleys contribute to the overall reliability and smooth operation of the conveyor system.
Conveyor systems are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, mining, logistics, and warehousing. Pulleys are essential components that ensure the efficient and reliable movement of materials and products along the conveyor belt, enabling automated and continuous material handling processes.

What is the importance of proper pulley alignment and tensioning?
Proper pulley alignment and tensioning are critical factors in ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of pulley systems. They play a significant role in maximizing power transmission, minimizing wear and tear, and maintaining the overall performance and longevity of the system. Here’s the importance of proper pulley alignment and tensioning:
1. Power Transmission Efficiency:
Proper pulley alignment and tensioning ensure optimal power transmission efficiency. When pulleys are misaligned or belts/chains are improperly tensioned, energy is wasted due to increased friction and slippage. This results in decreased power transfer and reduced system efficiency. By aligning the pulleys parallel to each other and applying the correct tension to the belts or chains, the system can achieve maximum power transmission, minimizing energy losses.
2. Belt/Chain Longevity:
Correct pulley alignment and tensioning contribute to the longevity of belts and chains. Misalignment and inadequate tension can cause uneven wear, excessive stretching, and premature failure of the belts or chains. Proper alignment and tension distribute the load evenly across the belts or chains, reducing stress and extending their lifespan. This helps to avoid unplanned downtime, maintenance costs, and the need for frequent belt/chain replacements.
3. Reduced Noise and Vibration:
Improper pulley alignment and tensioning can lead to increased noise and vibration in the system. Misaligned pulleys or loose belts/chains can cause excessive vibration, resulting in noise, equipment damage, and discomfort to operators or nearby personnel. Proper alignment and tensioning help minimize vibration, ensuring quieter operation and a more comfortable working environment.
4. System Reliability and Safety:
Proper alignment and tensioning contribute to the overall reliability and safety of pulley systems. Misaligned pulleys or loose belts/chains can lead to unexpected failures, breakdowns, or accidents. Over-tensioning can also cause excessive stress on components and increase the risk of system failures. By maintaining proper alignment and tension, the system operates within its design parameters, reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures and ensuring the safety of operators and equipment.
5. Improved Performance:
Correct pulley alignment and tensioning enhance the overall performance of the system. Properly tensioned belts or chains provide better grip and traction, allowing for smoother and more precise movement of the driven components. This results in improved speed control, reduced slippage, and enhanced accuracy in applications such as conveyor systems, machine tools, and automotive engines.
6. Maintenance and Cost Savings:
Proper pulley alignment and tensioning can lead to significant maintenance and cost savings. Well-aligned pulleys and correctly tensioned belts or chains experience less wear and require fewer adjustments. This reduces the frequency of maintenance tasks, such as belt/chain replacements, realignments, and re-tensioning. Additionally, by maximizing power transmission efficiency and minimizing wear, proper alignment and tensioning help reduce energy consumption and lower operating costs.
In conclusion, proper pulley alignment and tensioning are crucial for achieving optimal power transmission efficiency, prolonging the lifespan of belts or chains, reducing noise and vibration, ensuring system reliability and safety, improving performance, and realizing maintenance and cost savings. It is essential to follow manufacturer guidelines and perform regular inspections and adjustments to maintain proper alignment and tension in pulley systems.

What materials are typically used to manufacture pulleys?
Pulleys are manufactured using a variety of materials, depending on the specific application and requirements. Here are some of the materials that are typically used to manufacture pulleys:
1. Metal Alloys: Metal alloys such as steel and cast iron are commonly used to manufacture pulleys. Steel pulleys offer excellent strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Cast iron pulleys are known for their high strength and resistance to impact and shock loads. Metal alloys are preferred in heavy-duty applications where strength and durability are critical.
2. Aluminum: Aluminum is widely used in pulley manufacturing due to its lightweight nature and corrosion resistance. Aluminum pulleys are commonly used in applications that require reduced weight, such as automotive engines, aircraft components, and light-duty machinery. They offer good strength-to-weight ratio and are suitable for applications where weight reduction is a priority.
3. Plastic: Various types of plastics, including nylon, polyurethane, and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), are used to manufacture pulleys. Plastic pulleys are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and offer good resistance to wear and abrasion. They are commonly used in applications where noise reduction, chemical resistance, or non-conductive properties are required. Plastic pulleys are frequently used in conveyor systems, packaging machinery, and small-scale equipment.
4. Composite Materials: Composite materials, such as fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) and carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP), are utilized in the manufacturing of pulleys. These materials offer high strength-to-weight ratios, excellent resistance to corrosion, and good fatigue resistance. Composite pulleys are commonly used in industries such as aerospace, marine, and sports equipment, where lightweight components with exceptional strength are required.
5. Ceramics: In certain specialized applications, pulleys made of ceramics like aluminum oxide (alumina) or silicon nitride are used. Ceramic pulleys offer exceptional hardness, high temperature resistance, and excellent wear resistance. They are primarily used in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, where extreme precision, chemical resistance, and resistance to high temperatures are crucial.
It’s important to note that the choice of material for pulley manufacturing depends on factors such as load capacity, operating conditions, environmental factors, and cost considerations. Manufacturers select materials that provide the necessary properties to meet the specific requirements of the application while considering factors such as strength, durability, weight, and cost.


editor by CX
2023-09-21