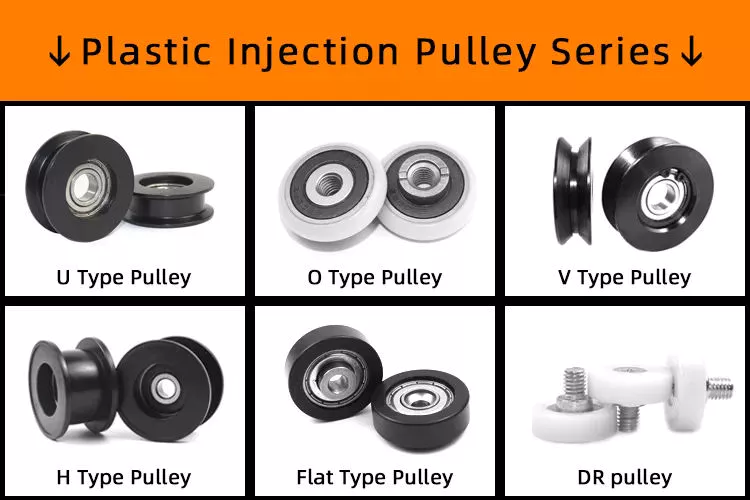
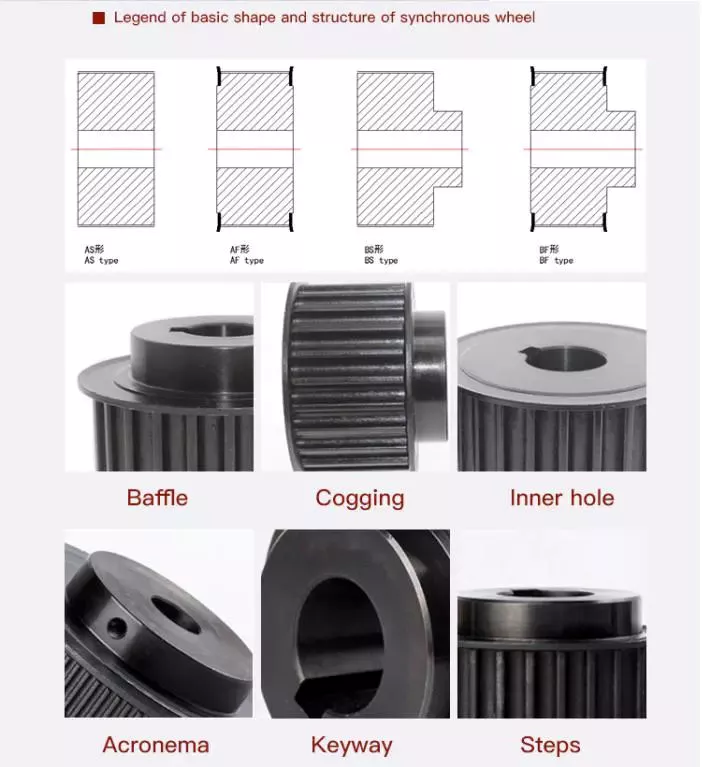
Product Description
Casting and Machining Belt Pulley for Italy customer
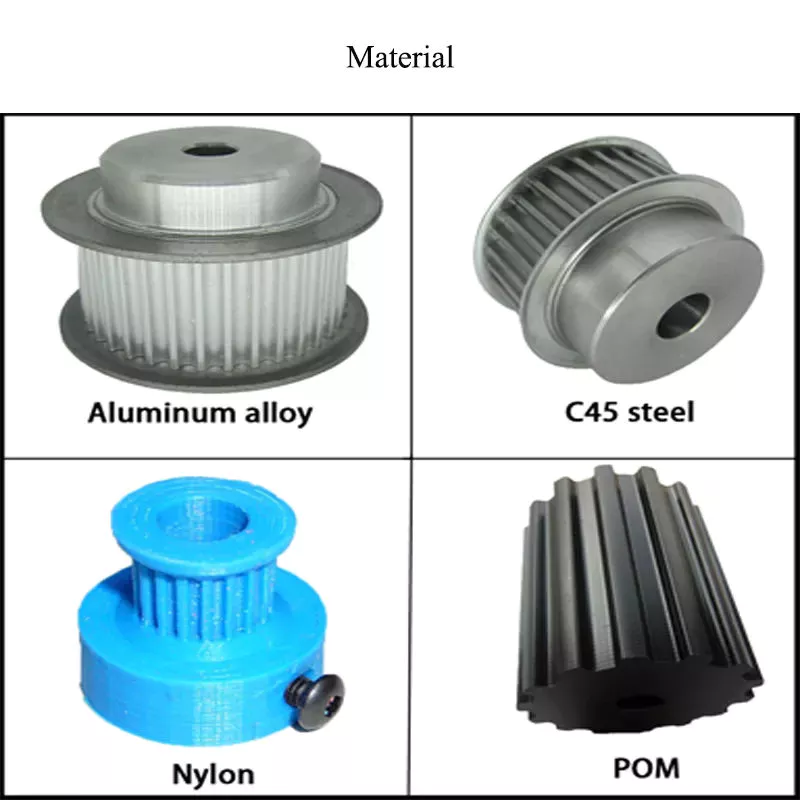
1. Material: Cast iron GG25, Ductile iron,grey iron
2. Process: machining – phosphating
3. Size:1C230,1C250,1C170,1B250,1B230
Specifications
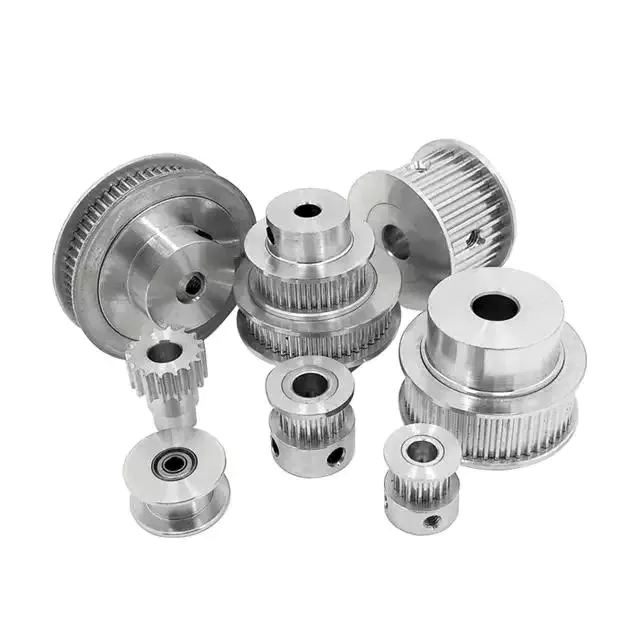
Various Types of Pulley GG20/GG25/GG30/V-Belt Pluuey
1.Produce as drawings
2.on time delivery
3.ISO,CCC Reliable qualit
Various Types of Pulley GG20/GG25/GG30/V-Belt pulley
Specifications:
Process: casting-machining-palstics spraying-packaging
Technical: sand casting
Material: China-HT200/HT250/HT300 Germery-GG20/GG25/GG30
Dimension: as customer’s request
Casting level: CT10-CT11
Surface roughness: Ra25
Packaging: wooden cases or as customer’s drawings
Surface treatment: shot blasting, plastic spraying, paint spraying
Equipment: cupola, electric furnace
Weight: 0.5kg-100kg
Surface colour: plastic spraying RAL2004/black paint/ antirust paint
Inspection:
In-house and third partyUniversal
All the products are strictly inspected by the operators and skilled QC
inspection tools: hardness tester, height ruler
Production Procedure:
Drawings→Mould developing→Raw casting→Sandblasting→Rough machining or finish machining→Surface treatment→Inspection→Packing→Delivery strictly
We can produce the pulleys according to the drawings and samples provided by the customers with excellent quality and competitive price.
As an experienced casting manufacturer, we assure you the quality! Our products are through careful inspection, and our quality is high and reliable which have been achieved cutomers’ satisfaction!
If you are interested in our products, please do not hesitate to contact us!
|
HangZhou Jiangdashengye Trade co.,ltd. |
|
|
OEM SERVICES |
|
|
Service |
Drawings or samples processing/OEM/ODM service provided |
|
Produce Process |
Drawings→ mould making →raw casting → sandblasting →rough machining or finish machining →surface treatment →product checking→ packing →delivering |
|
Casting Material |
Cast Iron, Grey Iron, Ductile Iron,Carbon Steel, Stainless steel, Alloy steel, |
|
Standard |
ISO, GB, ASTM, DIN, JIS |
|
Equipment |
melting furnace, centrifugal casting machines coated CHINAMFG machine CNC machines turning machines grinding machines milling machines drilling machine punching machines laser carving machine |
|
Surface treatment |
Heat treatment, Polishing, Sand blasting, Painting, Electro-plating, Chemical Plating, and other machining processing. |
|
Inspection Equipments |
Spectrum analysis instrument, Metallurgical analysis, Tensile strength tester, Hardness tester, Roughness tester, deflection tester, Impact test machine, Projector, Altimeter, Scale Micrometer, pressure tester, etc. |
|
Delivery |
Sample sent to customer by air. Large quantity products delivered to customer by sea from xingang,China |
|
Payment terms |
L/C at sight or 30% T/T as deposit and balanced 70% to pay before |
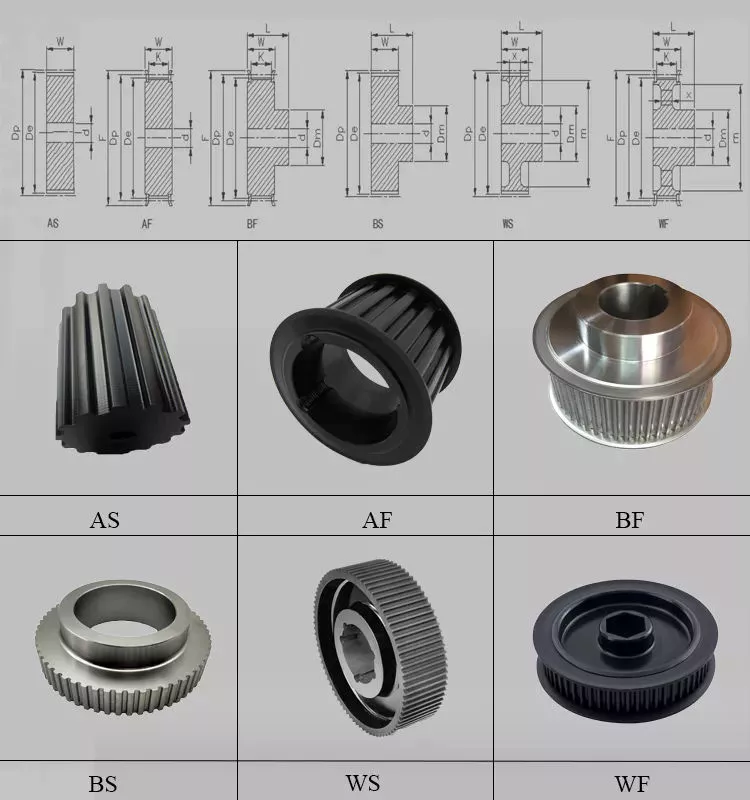
v pulley, v belt pulley, v groove pulley, v groove belt pulley, taper lock pulley, taper lock v belt pulley, taper lock bushing pulley, taper lock pulleys / taper bore pulley, large v belt pulley, double v belt pulley, cast iron v belt pulley belt pulley, variable speed v belt pulleys, v belt pulley split pulley, cast iron v belt pulley
V belt pulley specifications:
1) European standard:
a) V-belt pulleys for taper bushings: SPZ, SPA, SPB, SPC; up to 10 grooves
b) Adjustable speed V-belt pulleys and variable speed pulleys
c) Flat belt pulleys and conveyor belt pulleys
2) American standard:
a) Sheaves for taper bushings: 3V, 5V, 8V
b) Sheaves for QD bushings: 3V, 5V, 8V
c) Sheaves for split taper bushings: 3V, 5V, 8V
d) Sheaves for 3L, 4L or A, and 5L or B belts: AK, AKH, 2AK, 2AKH, BK, BKH,2BK, 2BKH, 3BK
e) Adjustable sheaves: poly V-pulley, multi-pitch H, L, J, K and M
3) Bore: pilot bore, finished bore, taper bore, bore for QD bushing
4) Surface finish: paint, phosphating, zinc plated
5) Material: cast iron, ductile iron, nylon, aluminum
6) Made according to drawings and/or samples, OEM inquiries welcomed
Now we send photo of our production as follows:
| Type: | Cargo Winch Strap |
|---|---|
| Certification: | GS |
| Size3: | 1b270 |
| Name: | Casting and Machining Belt Pulley |
| Size4: | 1b250 |
| Size2: | 1c230 |
| Samples: |
US$ 3.5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the common problems and maintenance requirements for pulleys?
Pulleys, like any mechanical component, can experience common problems and require regular maintenance to ensure their proper functioning and longevity. Here are some of the common problems and maintenance requirements for pulleys:
1. Wear and Tear: Over time, pulleys can experience wear and tear due to friction, load stress, and environmental factors. This can result in issues such as worn grooves, cracked or deformed pulley bodies, or damaged bearings. Regular inspection is necessary to identify signs of wear and address them promptly.
2. Misalignment: Pulleys can become misaligned, causing the belt or rope to run off its intended path. This can lead to inefficient power transmission, increased wear on the belt, and reduced overall system performance. Regular alignment checks and adjustments are necessary to ensure proper alignment of pulleys and belts.
3. Belt Tension: Proper belt tension is crucial for optimal pulley performance. Over time, belts can stretch or become loose, resulting in inadequate tension. Insufficient tension can cause slippage, reduced power transfer, and premature wear. Regular checks and adjustments of belt tension are necessary to maintain optimal performance.
4. Contamination: Pulleys can accumulate dirt, dust, debris, or other contaminants, particularly in industrial or outdoor environments. Contamination can lead to increased friction, reduced efficiency, and accelerated wear. Regular cleaning of pulleys is necessary to prevent buildup and maintain smooth operation.
5. Lubrication: Pulleys with bearings require proper lubrication to minimize friction and ensure smooth rotation. Insufficient lubrication can lead to increased friction, heat generation, and premature bearing failure. Regular lubrication according to manufacturer recommendations is essential for optimal pulley performance and longevity.
6. Bearing Maintenance: Pulleys with bearings should undergo regular bearing maintenance. This includes inspecting bearings for signs of wear or damage, cleaning them, and replacing worn-out or faulty bearings. Proper bearing maintenance helps prevent bearing failure, which can lead to pulley malfunction or system downtime.
7. Environmental Factors: Pulleys used in outdoor or harsh environments may be exposed to adverse conditions such as extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, or corrosive substances. Extra care should be taken to protect pulleys from these environmental factors. This may involve using appropriate seals, covers, or coatings and implementing preventive measures to mitigate the effects of the environment.
8. Regular Inspections: Regular inspections are crucial for identifying potential problems early on. Inspect pulleys for signs of wear, damage, misalignment, or other issues. Address any identified problems promptly to prevent further damage or system failure.
9. Replacement of Worn-out Parts: If any components of the pulley, such as the belt, bearings, or fasteners, are worn out or damaged beyond repair, they should be replaced promptly. Using worn-out parts can compromise the performance and safety of the pulley system.
10. Manufacturer Guidelines: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance and servicing of pulleys. Manufacturers often provide specific instructions on maintenance intervals, lubrication requirements, and other important considerations.
By proactively addressing these common problems and adhering to regular maintenance requirements, pulley performance and service life can be optimized, ensuring smooth and reliable operation in various applications.

How do pulleys work in garage door openers and winches?
Pulleys play a crucial role in both garage door openers and winches, enabling the smooth and efficient operation of these devices. They provide mechanical advantage, facilitate load lifting and lowering, and contribute to the overall functionality and safety of garage door openers and winches. Here’s how pulleys work in each of these applications:
1. Garage Door Openers:
In a typical garage door opener system, pulleys are used in conjunction with a motor, drive belt or chain, and a set of cables or torsion springs. The pulleys are mounted on the garage door’s torsion bar or header, and the cables or springs are connected to the bottom of the door. Here’s how the pulleys work in a garage door opener:
– Motor and Drive Mechanism: The motor drives a pulley or sprocket, which is connected to a drive belt or chain. As the motor rotates the pulley, the drive belt or chain moves, transferring rotational motion to another pulley or sprocket mounted on the torsion bar.
– Torsion Bar and Cables: The torsion bar, equipped with a pulley, is located above the garage door. The cables are threaded through the pulleys and attached to the bottom of the door on each side. When the motor rotates the torsion bar pulley, the cables move, causing the garage door to open or close.
– Mechanical Advantage: By using pulleys, the garage door opener system creates a mechanical advantage. The arrangement of the pulleys and cables or springs helps distribute the load, making it easier for the motor to lift the heavy garage door. This mechanical advantage reduces the strain on the motor and ensures smooth and controlled movement of the door.
2. Winches:
Pulleys are also integral components of winches used for lifting and pulling heavy loads. Winches consist of a drum or spool around which a cable or rope is wrapped, and pulleys are used to guide and redirect the cable or rope. Here’s how pulleys work in a winch:
– Load Lifting: The cable or rope is wound around the winch drum, and one end is attached to the load to be lifted or pulled. The other end is connected to a fixed point or a secondary pulley system. As the winch drum rotates, the cable or rope is wound or unwound, allowing the load to be lifted or lowered.
– Pulley Systems: Pulleys are used in winches to redirect the cable or rope, providing a mechanical advantage and ensuring smooth movement. Additional pulleys may be employed to create a block and tackle system, further increasing the mechanical advantage and the winch’s lifting capacity.
– Control and Safety: Winches often incorporate braking systems and clutches to control the movement and secure the load. Pulleys play a role in these control mechanisms, helping to regulate the winch’s speed and provide reliable stopping and holding power.
Overall, pulleys are essential components in garage door openers and winches, enabling the smooth and controlled movement of heavy loads. They provide mechanical advantage, facilitate load lifting and lowering, and contribute to the efficiency and safety of these devices.

How do pulleys contribute to load distribution and lifting?
Pulleys play a crucial role in load distribution and lifting by providing mechanical advantage and distributing the load over multiple segments of rope or belt. Here’s how pulleys contribute to load distribution and lifting:
1. Mechanical Advantage: Pulleys provide mechanical advantage, which allows for the multiplication of the force applied to the rope or belt. When a force is applied to one end of the rope or belt, it creates tension that causes the pulley to rotate. As the pulley turns, the force is transmitted to the load attached to the other end of the rope or belt. By distributing the load over multiple pulleys, the force required to lift the load is reduced, making it easier to lift heavier objects.
2. Load Sharing: Pulleys enable load sharing among multiple segments of the rope or belt. In systems with multiple pulleys, such as block and tackle arrangements, the load is distributed over several segments of rope or belt. Each segment carries a fraction of the load, reducing the strain on each individual segment. Load sharing ensures that the load is evenly distributed, minimizing the risk of overload or failure in any single segment.
3. Directional Change: Pulleys allow for directional change in the force applied to the load. By redirecting the force along a different path, pulleys enable lifting and moving loads in various directions, including vertically, horizontally, or at an angle. This directional change is particularly useful in situations where the force needs to be applied from a different position or angle than the original force application.
4. Balance and Stability: Pulleys contribute to load distribution and lifting by providing balance and stability. The use of multiple pulleys in a system helps to distribute the load evenly, preventing excessive stress on any single point. This balanced distribution of the load enhances stability and reduces the risk of tipping or imbalance during lifting operations.
5. Control and Precision: Pulleys provide control and precision in load distribution and lifting. By adjusting the tension in the rope or belt, operators can achieve precise positioning and movement of the load. This level of control allows for accurate placement of heavy objects and ensures smooth and controlled lifting operations.
6. Increased Lifting Capacity: By leveraging mechanical advantage and load distribution, pulleys increase the lifting capacity. The mechanical advantage gained through the use of pulleys allows for the lifting of heavier loads with less effort. The load is distributed over multiple segments of rope or belt, reducing the force required to lift the load and enabling the lifting of objects that would otherwise be too heavy to lift manually.
Overall, pulleys contribute to load distribution and lifting by providing mechanical advantage, load sharing, directional change, balance and stability, control and precision, and increased lifting capacity. These contributions make pulleys an essential component in various lifting and load handling applications.


editor by CX
2023-09-19