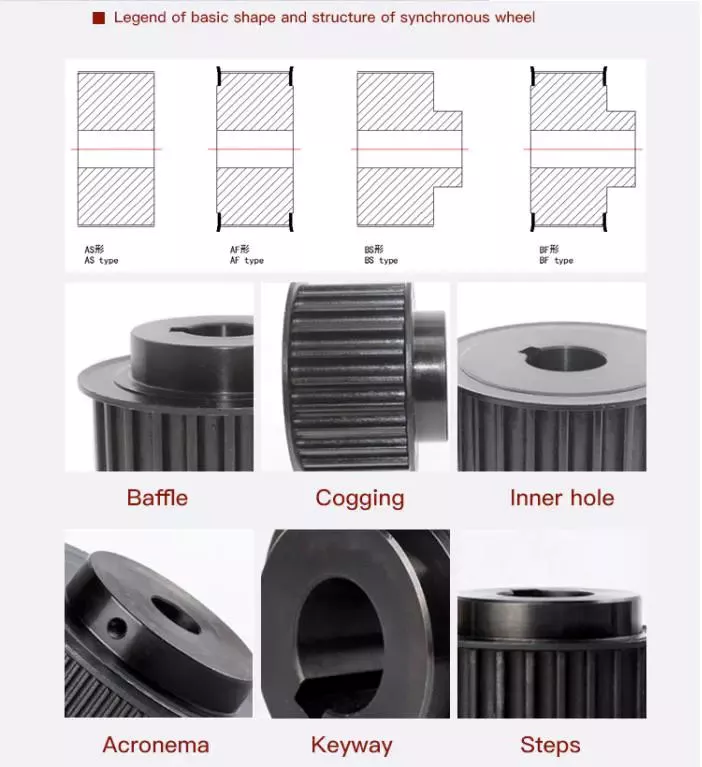
Product Description
CHINAMFG Machinery offers a wide range of high quality Timing Belt Pulleys and Toothed Bars / Timing Bars. Standard and non-standard pulleys according to drawings are available.
Types of material:
1. AlCuMgPb 6061 6082 Aluminum Timing Pulley
2. C45E 1045 S45C Carbon Steel Timing Pulley
3. GG25 HT250 Cast Iron Timing Pulley
4. SUS303 SUS304 AISI431 Stainless Steel Timing Pulley
5. Other material on demand, such as cooper, bronze and plastic
Types of surface treatment
1. Anodized surface -Aluminum Pulleys
2. Hard anodized surface — Aluminum Pulleys
3. Black Oxidized surface — Steel Pulleys
4. Zinc plated surface — Steel Pulleys
5. Chromate surface — Steel Pulleys; Cast Iron Pulleys
6. Nickel plated surface –Steel Pulleys; Cast Iron Pulleys
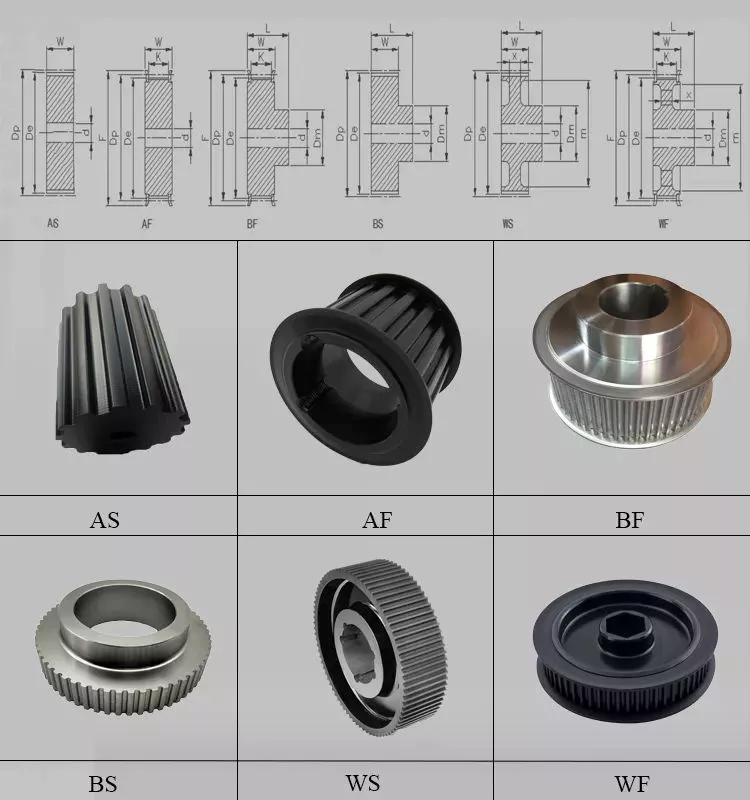
Types of teeth profile
| Teeth Profile | Pitch |
| HTD | 3M,5M,8M,14M,20M |
| AT | AT5,AT10,AT20 |
| T | T2.5,T5,T10 |
| MXL | 0.08″(2.032MM) |
| XL | 1/5″(5.08MM) |
| L | 3/8″(9.525MM) |
| H | 1/2″(12.7MM) |
| XH | 7/8″(22.225MM) |
| XXH | 1 1/4″(31.75MM) |
| STS STPD | S2M,S3M,S4.5M,S5M,S8M,S14M |
| RPP | RPP5M,RPP8M,RPP14M,RPP20M |
| PGGT | PGGT 2GT, 3GT and 5GT |
| PCGT | GT8M,GT14M |
Types of pitches and sizes
Imperial Inch Timing Belt Pulley,
1. Pilot Bore MXL571 for 6.35mm timing belt; teeth number from 16 to 72;
2. Pilot Bore XL037 for 9.53mm timing belt; teeth number from 10 to 72;
3. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore L050 for 12.7mm timing belt; teeth number from 10 to 120;
4. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore L075 for 19.05mm timing belt; teeth number from 10 to 120;
5. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore L100 for 25.4mm timing belt; teeth number from 10 to 120;
6. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore H075 for 19.05mm timing belt; teeth number from 14 to 50;
7. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore H100 for 25.4mm timing belt; teeth number from 14 to 156;
8. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore H150 for 38.1mm timing belt; teeth number from 14 to 156;
9. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore H200 for 50.8mm timing belt; teeth number from 14 to 156;
10. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore H300 for 76.2mm timing belt; teeth number from 14 to 156;
11. Taper Bore XH200 for 50.8mm timing belt; teeth number from 18 to 120;
12. Taper Bore XH300 for 76.2mm timing belt; teeth number from 18 to 120;
13. Taper Bore XH400 for 101.6mm timing belt; teeth number from 18 to 120;
Metric Timing Belt Pulley T and AT
1. Pilot Bore T2.5-16 for 6mm timing belt; teeth number from 12 to 60;
2. Pilot Bore T5-21 for 10mm timing belt; teeth number from 10 to 60;
3. Pilot Bore T5-27 for 16mm timing belt; teeth number from 10 to 60;
4. Pilot Bore T5-36 for 25mm timing belt; teeth number from 10 to 60;
5. Pilot Bore T10-31 for 16mm timing belt; teeth number from 12 to 60;
6. Pilot Bore T10-40 for 25mm timing belt; teeth number from 12 to 60;
7. Pilot Bore T10-47 for 32mm timing belt; teeth number from 18 to 60;
8. Pilot Bore T10-66 for 50mm timing belt; teeth number from 18 to 60;
9. Pilot Bore AT5-21 for 10mm timing belt; teeth number from 12 to 60;
10. Pilot Bore AT5-27 for 16mm timing belt; teeth number from 12 to 60;
11. Pilot Bore AT5-36 for 25mm timing belt; teeth number from 12 to 60;
12. Pilot Bore AT10-31 for 16mm timing belt; teeth number from 15 to 60;
13. Pilot Bore AT10-40 for 25mm timing belt; teeth number from 15 to 60;
14. Pilot Bore AT10-47 for 32mm timing belt; teeth number from 18 to 60;
15. Pilot Bore AT10-66 for 50mm timing belt; teeth number from 18 to 60;
Metric Timing Belt Pulley HTD3M, 5M, 8M, 14M
1. HTD3M-06; 3M-09; 3M-15; teeth number from 10 to 72;
2. HTD5M-09; 5M-15; 5M-25; teeth number from 12 to 72;
3. HTD8M-20; 8M-30; 8M-50; 8M-85 teeth number from 22 to 192;
4. HTD14M-40; 14M-55; 14M-85; 14M-115; 14M-170; teeth number from 28-216;
5. Taper Bore HTD5M-15; 8M-20; 8M-30; 8M-50; 8M-85; 14M-40; 14M-55; 14M-85;
14M-115; 14M-170
Metric Timing Belt Pulleys for Poly Chain GT2 Belts
1. PCGT8M-12; PCGT8M-21; PCGT8M-36; PCGT8M-62;
2. PCGT14M-20; PCGT14M-37; PCGT14M-68; PCGT14M-90; PCGT14M-125;
Power Grip CHINAMFG Tooth/ PGGT 2GT, 3GT and 5GT
1. 2GT-06, 2GT-09 for timing belt width 6mm and 9mm
2. 3GT-09, 3GT-15 for timing belt width 9mm and 15mm
3. 5GT-15, 5GT-25 for timing belt width 15mm and 25mm
OMEGA RPP HTD Timing Pulleys
1. RPP3M-06; 3M-09; 3M-15; teeth number from 10 to 72;
2. RPP5M-09; 5M-15; 5M-25; teeth number from 12 to 72;
3. RPP8M-20; 8M-30; 8M-50; 8M-85 teeth number from 22 to 192;
4. RPP14M-40; 14M-55; 14M-85; 14M-115; 14M-170; teeth number from 28-216;
5. Taper Bore RPP5M-15; 8M-20; 8M-30; 8M-50; 8M-85; 14M-40; 14M-55; 14M-85;
14M-115; 14M-170 .
Ubet Machinery is also competetive on these power transmission components.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | ISO |
|---|---|
| Pulley Sizes: | Timing |
| Manufacturing Process: | Sawing |
| Samples: |
US$ 3/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample Normally sample order can be ready in 15 days
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What are the common problems and maintenance requirements for pulleys?
Pulleys, like any mechanical component, can experience common problems and require regular maintenance to ensure their proper functioning and longevity. Here are some of the common problems and maintenance requirements for pulleys:
1. Wear and Tear: Over time, pulleys can experience wear and tear due to friction, load stress, and environmental factors. This can result in issues such as worn grooves, cracked or deformed pulley bodies, or damaged bearings. Regular inspection is necessary to identify signs of wear and address them promptly.
2. Misalignment: Pulleys can become misaligned, causing the belt or rope to run off its intended path. This can lead to inefficient power transmission, increased wear on the belt, and reduced overall system performance. Regular alignment checks and adjustments are necessary to ensure proper alignment of pulleys and belts.
3. Belt Tension: Proper belt tension is crucial for optimal pulley performance. Over time, belts can stretch or become loose, resulting in inadequate tension. Insufficient tension can cause slippage, reduced power transfer, and premature wear. Regular checks and adjustments of belt tension are necessary to maintain optimal performance.
4. Contamination: Pulleys can accumulate dirt, dust, debris, or other contaminants, particularly in industrial or outdoor environments. Contamination can lead to increased friction, reduced efficiency, and accelerated wear. Regular cleaning of pulleys is necessary to prevent buildup and maintain smooth operation.
5. Lubrication: Pulleys with bearings require proper lubrication to minimize friction and ensure smooth rotation. Insufficient lubrication can lead to increased friction, heat generation, and premature bearing failure. Regular lubrication according to manufacturer recommendations is essential for optimal pulley performance and longevity.
6. Bearing Maintenance: Pulleys with bearings should undergo regular bearing maintenance. This includes inspecting bearings for signs of wear or damage, cleaning them, and replacing worn-out or faulty bearings. Proper bearing maintenance helps prevent bearing failure, which can lead to pulley malfunction or system downtime.
7. Environmental Factors: Pulleys used in outdoor or harsh environments may be exposed to adverse conditions such as extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, or corrosive substances. Extra care should be taken to protect pulleys from these environmental factors. This may involve using appropriate seals, covers, or coatings and implementing preventive measures to mitigate the effects of the environment.
8. Regular Inspections: Regular inspections are crucial for identifying potential problems early on. Inspect pulleys for signs of wear, damage, misalignment, or other issues. Address any identified problems promptly to prevent further damage or system failure.
9. Replacement of Worn-out Parts: If any components of the pulley, such as the belt, bearings, or fasteners, are worn out or damaged beyond repair, they should be replaced promptly. Using worn-out parts can compromise the performance and safety of the pulley system.
10. Manufacturer Guidelines: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance and servicing of pulleys. Manufacturers often provide specific instructions on maintenance intervals, lubrication requirements, and other important considerations.
By proactively addressing these common problems and adhering to regular maintenance requirements, pulley performance and service life can be optimized, ensuring smooth and reliable operation in various applications.
What is the role of pulleys in the mining and construction industries?
Pulleys play a vital role in the mining and construction industries, where they are utilized in various applications to facilitate heavy-duty operations, enhance safety, and improve efficiency. Here’s an overview of the role of pulleys in these industries:
1. Conveyor Systems:
In mining and construction, conveyor systems are extensively used to transport bulk materials, such as ores, rocks, gravel, and construction aggregates. Pulleys are integral components of conveyor systems, guiding and supporting the conveyor belts or chains. They help in maintaining tension, reducing friction, and ensuring smooth movement of materials over long distances. The pulleys used in these systems are designed to withstand high loads and harsh environmental conditions.
2. Hoisting and Lifting Equipment:
Pulleys are crucial in hoisting and lifting equipment used in mining and construction activities. Cranes, winches, and lifting systems often incorporate pulley arrangements to provide mechanical advantage and control the movement of heavy loads. The pulleys, along with ropes, cables, or chains, allow for safe and efficient lifting, lowering, and positioning of equipment, materials, and structures at construction sites or in mining operations.
3. Wire Rope Systems:
In mining and construction, wire ropes are extensively used for various applications, including hauling, towing, and lifting heavy loads. Pulleys, known as sheaves, are employed in wire rope systems to guide and redirect the wire ropes. The sheaves help in maintaining proper alignment, reducing wear, and ensuring efficient power transmission. They are commonly used in applications such as cranes, elevators, and wire rope hoists.
4. Crushing and Screening Equipment:
In the mining and construction industries, pulleys are used in crushing and screening equipment. For example, in crushers, pulleys are utilized to drive the rotating motion of the crusher’s jaws or cones, enabling the crushing of large rocks or ores into smaller sizes. Pulleys also play a role in vibrating screens, helping to generate the necessary vibrations that separate and classify materials based on size.
5. Earthmoving and Excavation Equipment:
Pulleys are incorporated into earthmoving and excavation equipment in mining and construction applications. For instance, in excavators or dragline machines, pulleys are used in the cable systems that control the movement of the bucket or shovel. The pulleys help in extending or retracting the cables, allowing for efficient excavation, loading, and material handling.
6. Tensioning and Alignment:
In mining and construction operations, pulleys are utilized for tensioning and alignment purposes. Tensioning pulleys ensure proper tensioning of belts, ropes, or cables, optimizing power transmission and preventing slippage. Alignment pulleys are employed to maintain the correct alignment of belts or chains, reducing wear, minimizing vibrations, and extending the lifespan of the components.
In summary, pulleys play a critical role in the mining and construction industries, contributing to material handling, lifting and hoisting operations, wire rope systems, crushing and screening equipment, earthmoving and excavation machinery, and tensioning and alignment applications. Their use enhances safety, improves efficiency, and enables the execution of heavy-duty tasks in these demanding industries.

How do pulleys contribute to load distribution and lifting?
Pulleys play a crucial role in load distribution and lifting by providing mechanical advantage and distributing the load over multiple segments of rope or belt. Here’s how pulleys contribute to load distribution and lifting:
1. Mechanical Advantage: Pulleys provide mechanical advantage, which allows for the multiplication of the force applied to the rope or belt. When a force is applied to one end of the rope or belt, it creates tension that causes the pulley to rotate. As the pulley turns, the force is transmitted to the load attached to the other end of the rope or belt. By distributing the load over multiple pulleys, the force required to lift the load is reduced, making it easier to lift heavier objects.
2. Load Sharing: Pulleys enable load sharing among multiple segments of the rope or belt. In systems with multiple pulleys, such as block and tackle arrangements, the load is distributed over several segments of rope or belt. Each segment carries a fraction of the load, reducing the strain on each individual segment. Load sharing ensures that the load is evenly distributed, minimizing the risk of overload or failure in any single segment.
3. Directional Change: Pulleys allow for directional change in the force applied to the load. By redirecting the force along a different path, pulleys enable lifting and moving loads in various directions, including vertically, horizontally, or at an angle. This directional change is particularly useful in situations where the force needs to be applied from a different position or angle than the original force application.
4. Balance and Stability: Pulleys contribute to load distribution and lifting by providing balance and stability. The use of multiple pulleys in a system helps to distribute the load evenly, preventing excessive stress on any single point. This balanced distribution of the load enhances stability and reduces the risk of tipping or imbalance during lifting operations.
5. Control and Precision: Pulleys provide control and precision in load distribution and lifting. By adjusting the tension in the rope or belt, operators can achieve precise positioning and movement of the load. This level of control allows for accurate placement of heavy objects and ensures smooth and controlled lifting operations.
6. Increased Lifting Capacity: By leveraging mechanical advantage and load distribution, pulleys increase the lifting capacity. The mechanical advantage gained through the use of pulleys allows for the lifting of heavier loads with less effort. The load is distributed over multiple segments of rope or belt, reducing the force required to lift the load and enabling the lifting of objects that would otherwise be too heavy to lift manually.
Overall, pulleys contribute to load distribution and lifting by providing mechanical advantage, load sharing, directional change, balance and stability, control and precision, and increased lifting capacity. These contributions make pulleys an essential component in various lifting and load handling applications.


editor by CX
2024-02-01