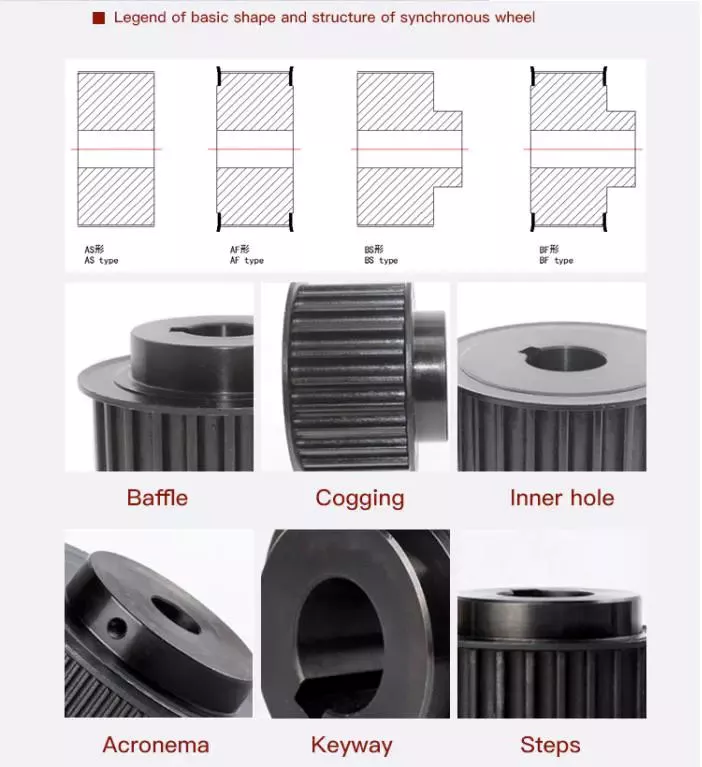
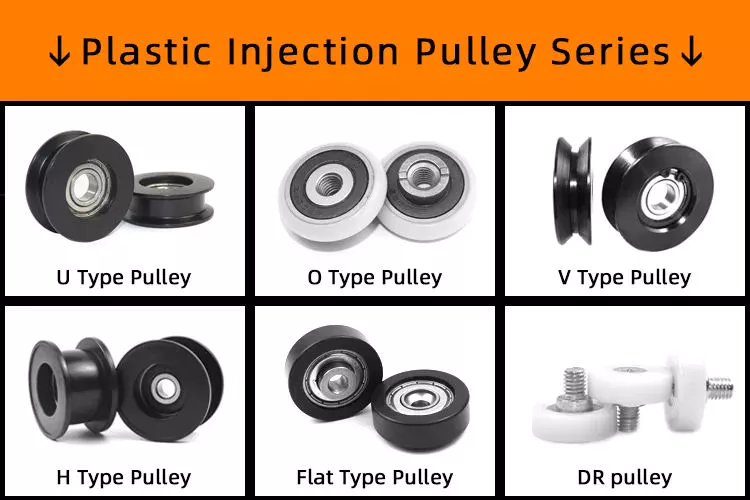
Product Description
Flat belt pulley block v timing belt pulley
V belt pulley specifications
· European standards :
a) V-belt pulley for taper bushing: SPZ, SPA, SPB, SPC
b) Adjustable speed V-belt pulleys and variable speed pulleys
c) Flat belt pulleys and conveyor belt pulleys
d) Have many models , cannot show all together here , need to know learn more ,contact us .
| 500 – 1 x SPZ – 2517 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 50 – 2 x SPZ – 1008 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 56 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 60 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 rü 26 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 63 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 67 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 71 – 2 x SPZ – 1108 | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 75 – 2 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 80 – 2 x SPZ – 1210 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 85 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 90 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 95 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 100 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 106 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 112 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 118 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 125 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 132 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 140 – 2 x SPZ – 1610 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 150 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 160 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 170 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 180 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 190 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| 200 – 2 x SPZ – 2012 bü | Taper-v-belt pulley |
| SPB-1 | ||||||
| PULLEY MODEL | TAPER BUSH | WEIGHT | F | R | L | P |
| SPB100-1 | 1610 | 0.9 | 25 | 25 | ||
| SPB106-1 | 1610 | 1.1 | 25 | 25 | ||
| SPB112-1 | 1610 | 1.2 | 25 | 25 | ||
| SPB118-1 | 1610 | 1.3 | 25 | 25 | ||
| SPB125-1 | 1610 | 1.5 | 25 | 25 | ||
| SPB132-1 | 1610 | 1.7 | 25 | 25 | ||
| SPB140-1 | 1610 | 1.8 | 25 | 25 | ||
| SPB150-1 | 1610 | 2.1 | 25 | 25 | ||
| SPB160-1 | 1610 | 2.5 | 25 | 25 | ||
| SPB170-1 | 1610 | 2.9 | 25 | 25 | ||
| SPB180-1 | 1610 | 3.2 | 25 | 25 | ||
| SPB190-1 | 2012 | 3.8 | 25 | 32 | 3.5 | |
| SPB200-1 | 2012 | 4.2 | 25 | 32 | 3.5 | |
| SPB212-1 | 2012 | 4.3 | 25 | 32 | 3.5 | |
| SPB224-1 | 2012 | 4.7 | 25 | 32 | 3.5 | |
| SPB236-1 | 2012 | 5.1 | 25 | 32 | 3.5 | |
| SPB250-1 | 2012 | 5.7 | 25 | 32 | 3.5 | |
| SPB280-1 | 2012 | 6 | 25 | 32 | 3.5 | |
| SPB300-1 | 2012 | 7.1 | 25 | 32 | 7 | |
| SPB315-1 | 2012 | 7.5 | 25 | 32 | 3.5 | |
FAQ
1.Q: What is your Trade term ?
A: FOB HangZhou Or HangZhou port
2.Q: Can you offer OEM ?
A: Yes , OEM are always welcomed . Please emial us relevant information .
3.Q: Can I get some samples before placing order ?
A: Yes, We will offer 1-2 pcs samples free of charge . Due to different situation , some samples will be charged . If you need further information about our sample policy , please contact us .
4.Q: What is your MOQ ?
A: MOQ of most our products is 1000 pcs , different items maybe different .
5.Q: How can you ensure the quality inspection?
A: On the order process,we have inspection standard before delivery and will supply you the pictures.
6. Q: What about the lead time for mass production ?
A: It depends on the order quantity and the season you place the order . In general , our lead time is about 15~25 days , depends on products
Our service :
Sample service:
-We provide free samples for our existing products range.
-Sample and tooling charges need if special design needed, the exact charges depends on your final design and product.
-We will return sample charges to you once place an order, and return the tooling charges once the order quantity reach to certain quantity.
-It will take 2-3days for free samples.
Customized services:
– We provide OEM and ODM process Service, also Provide product sketch.
After-sale services:
– For most of our products, we provide one year warranty.If any items broken for unartificial reason, we can replace the items after having the approve. We guarantee your satisfaction with all our merchandise. The feedbacks will be paid more attentions from customers constant, we will solve the problems timely.
| Certification: | ISO |
|---|---|
| Pulley Sizes: | OEM |
| Manufacturing Process: | Casting |
| Material: | Iron |
| Surface Treatment: | Polishing |
| Application: | Chemical Industry, Grain Transport, Mining Transport, Power Plant, OEM |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
What is the difference between a fixed and a swivel pulley?
Fixed and swivel pulleys are two common types of pulleys that differ in their design and functionality. Here are the key differences between these two types:
1. Fixed Pulley: A fixed pulley is a type of pulley that is mounted or attached to a fixed point, such as a beam or a ceiling. It does not move or rotate independently of its mounting point. The primary function of a fixed pulley is to change the direction of the force applied to a rope or cable. When a force is applied to the rope or cable passing through a fixed pulley, the load moves in the opposite direction. However, a fixed pulley does not provide any mechanical advantage, meaning it does not reduce the effort required to lift the load.
2. Swivel Pulley: A swivel pulley, also known as a movable pulley, is designed to rotate or swivel on a separate mounting point. It has a built-in mechanism that allows it to move independently. Unlike a fixed pulley, a swivel pulley is capable of changing both the direction and the magnitude of the force applied to the rope or cable. When a force is applied to the rope or cable passing through a swivel pulley, the load moves in the same direction as the applied force. Additionally, a swivel pulley provides a mechanical advantage by distributing the load’s weight over multiple strands of rope or cable, reducing the effort required to lift the load.
In summary, the main differences between fixed and swivel pulleys are:
– Fixed pulleys are stationary and do not move independently, while swivel pulleys can rotate or swivel on a separate mounting point.
– Fixed pulleys change the direction of the force applied to the rope or cable, while swivel pulleys change both the direction and the magnitude of the force.
– Fixed pulleys do not provide a mechanical advantage, while swivel pulleys provide a mechanical advantage by distributing the load’s weight over multiple strands of rope or cable.
Both fixed and swivel pulleys have their specific applications and can be used individually or in combination with each other to achieve desired mechanical functions in various systems and setups.
Can pulleys be used for both horizontal and vertical lifting?
Yes, pulleys can be used for both horizontal and vertical lifting. The versatility of pulley systems allows them to be utilized in various lifting applications, regardless of the direction of the load. Here’s how pulleys can be used for horizontal and vertical lifting:
1. Horizontal Lifting: In horizontal lifting scenarios, pulleys can be employed to change the direction of the force applied to the load. By using a combination of fixed and movable pulleys, the force can be redirected to pull the load horizontally. This is commonly seen in applications such as manual hoists or block and tackle systems used in construction, where heavy objects need to be moved horizontally across distances.
2. Vertical Lifting: Pulleys are widely used in vertical lifting applications, such as cranes, elevators, and lifting systems. In these setups, the pulleys are typically arranged in such a way that the load can be lifted vertically. By using multiple pulleys and ropes or cables, mechanical advantage can be achieved, making lifting heavier loads easier. The pulleys distribute the load’s weight across multiple lines, reducing the effort required to lift the load.
It’s worth noting that the number and arrangement of pulleys can vary depending on the specific lifting requirements. For example, a single fixed pulley can change the direction of the force but does not provide any mechanical advantage. On the other hand, systems with multiple pulleys, such as compound pulley systems or block and tackle setups, can provide significant mechanical advantage, making lifting heavier loads more manageable.
Whether it is horizontal or vertical lifting, the principles of pulley mechanics remain the same. Pulleys allow for force redirection, mechanical advantage, and load distribution, making lifting tasks more efficient and manageable. The specific configuration and setup of the pulley system will depend on the lifting requirements and the desired level of mechanical advantage.

What is a pulley, and how does it function in mechanical systems?
A pulley is a simple machine consisting of a grooved wheel and a rope, cable, or belt that runs along the groove. It is used to transmit force and motion in mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a pulley functions:
1. Mechanical Advantage: The primary function of a pulley is to provide mechanical advantage. By changing the direction of the force applied and distributing it over multiple segments of the rope or belt, a pulley system allows for easier lifting or moving of heavy loads. The mechanical advantage gained depends on the number of pulleys used in the system.
2. Force Transmission: When a force is applied to one end of the rope or belt, it creates tension that causes the pulley to rotate. As the pulley turns, the force is transmitted to the load attached to the other end of the rope or belt. This force transmission allows for the movement and manipulation of objects in mechanical systems.
3. Directional Change: One of the key functions of a pulley is to change the direction of the applied force. By redirecting the force along a different path, a pulley system enables the operator to exert force from a more convenient or advantageous position. This directional change is particularly useful in situations where the force needs to be applied vertically, horizontally, or at an angle.
4. Speed and Torque Conversion: In addition to changing the direction of force, pulleys can also be used to convert speed and torque in mechanical systems. By varying the size of the pulleys or using pulleys of different diameters, the rotational speed and torque can be adjusted according to the requirements of the system. This speed and torque conversion allows for the optimization of power transmission and the matching of different rotational speeds between input and output components.
5. Multiple Pulley Systems: Pulleys can be combined in systems to achieve increased mechanical advantage or to create complex motion patterns. In systems with multiple pulleys, such as block and tackle arrangements, the load is distributed over several segments of rope or belt, further reducing the effort required to lift heavy objects. These systems are often used in cranes, elevators, and other applications where heavy lifting is necessary.
6. Fixed and Movable Pulleys: Pulleys can be categorized as fixed or movable. A fixed pulley is attached to a stationary structure, and its main function is to change the direction of force. A movable pulley, on the other hand, is attached to the load being moved and moves with it. Movable pulleys provide mechanical advantage by reducing the effort required to lift the load.
7. Belt and Rope Pulleys: Pulleys can have different designs depending on the application. Belt pulleys typically have a grooved surface to grip and guide belts, while rope pulleys have a smooth surface to minimize friction and prevent rope wear. The choice between belt and rope pulleys depends on factors such as load requirements, operational environment, and desired efficiency.
Overall, a pulley is a versatile mechanical device that functions as a force multiplier, directional changer, and speed/torque converter in mechanical systems. Its ability to provide mechanical advantage, change force direction, and facilitate complex motion patterns makes it an essential component in various applications, including lifting, transportation, and power transmission.


editor by CX
2023-11-07